In this laravel 12 tutorial, you will learn how to upload multiple files in laravel api using postman step by step complete guide with example.
Uploading multiple files through a Laravel API is a common requirement in modern web applications, whether you’re building a gallery app, document management system, or any platform that handles user-generated content. This comprehensive guide walks you through creating a Laravel API endpoint that accepts multiple file uploads, validates them properly, and stores them securely—all while testing with Postman.
Table of Contents
What You’ll Learn
By the end of this tutorial, you’ll understand how to create a fully functional Laravel API endpoint for multiple file uploads with proper validation rules, error handling, and how to test everything using Postman.
Prerequisites
Before we begin, make sure you have the following installed and configured:
- Laravel 12 (or Laravel 9+) installed and configured
- Postman installed for API testing
- Basic understanding of Laravel routing and controllers
- PHP 8.1 or higher
- Composer installed
- MySQL or any other supported database
Step 1: Create the Files Table and Model
To track uploaded files in your database, we’ll create a migration and model. Run the following commands:
php artisan make:model File -m
This creates:
- A File model at app/Models/File.php
- A migration file in database/migrations/xxxx_create_files_table.php
Open the migration file in database/migrations/xxxx_create_files_table.php and update it with the following schema:
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
return new class extends Migration
{
/**
* Run the migrations.
*/
public function up(): void
{
Schema::create('files', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('name'); // Unique filename stored on disk
$table->string('url'); // Publicly accessible
$table->timestamps();
});
}
/**
* Reverse the migrations.
*/
public function down(): void
{
Schema::dropIfExists('files');
}
};
Now, Open app/Models/File.php and add the following code:
<?php
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class File extends Model
{
/**
* The attributes that are mass assignable.
*
* @var array<int, string>
*/
protected $fillable = [
'name',
'url',
];
}
Run the Migration
Execute the migration to create the files table in your database:
php artisan migrate
Read Also : Laravel 12 Display Image From Storage Folder
Step 2: Set Up Storage Configuration
Laravel provides a powerful filesystem abstraction that makes it easy to work with local filesystems and cloud storage services. Before uploading files, ensure your storage is properly configured.
Configure the Public Disk
Open config/filesystems.php and verify the public disk configuration:
// ... other configurations
'disks' => [
// ... other configurations
'public' => [
'driver' => 'local',
'root' => storage_path('app/public'),
'url' => env('APP_URL').'/storage',
'visibility' => 'public',
'throw' => false,
'report' => false,
],
// ... other configurations
],
// ... other configurations
The public disk is intended for files that should be publicly accessible, making it perfect for user uploads like images and documents.
Create a Symbolic Link
Run this Artisan command to create a symbolic link from public/storage to storage/app/public:
php artisan storage:link
This command creates a symbolic link that allows publicly accessible files to be easily accessed through the web.
Step 3: Create API Routes
Open routes/api.php and add the following route for file uploads:
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
use App\Http\Controllers\FileController;
Route::post('/upload-files', [FileController::class, 'uploadMultipleFiles']);
This creates a POST endpoint at /api/upload-files that will handle our multiple file uploads.
Read Also : Laravel 12 Array Validation Example
Step 4: Create Controller & Upload Logic with Validation
First, let’s create a dedicated controller to handle our file uploads. Open your terminal and run the following Artisan command:
php artisan make:controller FileController
This creates a new controller file at app/Http/Controllers/FileController.php.
Now let’s implement the controller method with comprehensive validation. Open app/Http/Controllers/FileController.php and add the following code:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Validator;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Storage;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Models\File;
class FileController extends Controller
{
public function uploadMultipleFiles(Request $request)
{
// Validate the incoming files
$validator = Validator::make($request->all(), [
'files' => 'required|array|min:1|max:10',
'files.*' => 'required|file|mimes:jpg,jpeg,png,pdf,docx,xlsx|max:5120',
], [
'files.required' => 'Please select at least one file to upload.',
'files.array' => 'Files must be sent as an array.',
'files.min' => 'You must upload at least one file.',
'files.max' => 'You cannot upload more than 10 files at once.',
'files.*.required' => 'Each file is required.',
'files.*.file' => 'Each upload must be a valid file.',
'files.*.mimes' => 'Only JPG, JPEG, PNG, PDF, DOCX, and XLSX files are allowed.',
'files.*.max' => 'Each file must not exceed 5MB in size.',
]);
// Check if validation fails
if ($validator->fails()) {
return response()->json([
'success' => false,
'message' => 'Validation errors occurred.',
'errors' => $validator->errors()
], 422);
}
// Process and store the files
$uploadedFiles = [];
if ($request->hasFile('files')) {
foreach ($request->file('files') as $file) {
// Generate a unique filename
$filename = time() . '_' . uniqid() . '.' . $file->getClientOriginalExtension();
// Store the file in the 'uploads' directory on the public disk
$path = $file->storeAs('uploads', $filename, 'public');
File::create([
'name' => $filename,
'url' => Storage::disk('public')->url($path),
]);
// Collect file information
$uploadedFiles[] = [
'name' => $filename,
'url' => Storage::disk('public')->url($path),
];
}
}
// Return success response
return response()->json([
'success' => true,
'message' => 'Files uploaded successfully.',
'data' => [
'total_files' => count($uploadedFiles),
'files' => $uploadedFiles
]
], 201);
}
}
Understanding the Validation Rules
Let’s break down the validation rules used in this example:
Array Validation
files => ‘required|array|min:1|max:10’: This ensures the files parameter is required, must be an array, contains at least 1 file, and no more than 10 files.
Individual File Validation
- files.* => ‘required|file|mimes:jpg,jpeg,png,pdf,docx,xlsx|max:5120’: The asterisk (*) notation validates each element in the array.
- required: Each file in the array must be present
- file: Validates that the upload is a valid file
- mimes: Restricts file types to specific extensions
- max:5120: Limits file size to 5120 KB (5MB)
Custom Validation Messages
Custom error messages make your API more user-friendly by providing clear feedback when validation fails. Each validation rule can have its own custom message, making debugging easier for API consumers.
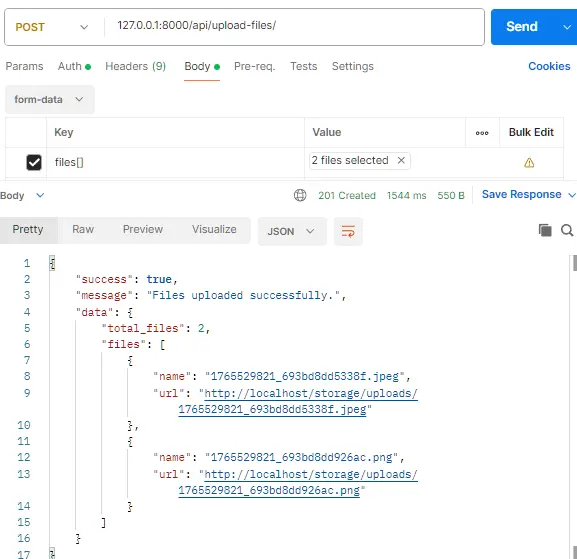
Step 5: Testing with Postman
Now that our API endpoint is ready, let’s test it using Postman.
- Open Postman and Create a New Request
- Set the Request Method and URL
- Method: Select POST from the dropdown
- URL: Enter http://localhost:8000/api/upload-files/
- Configure the Body
- Add File Fields
- In the KEY column, enter files[]
- Hover over the KEY field and click the dropdown that appears on the right
- Select File instead of Text
- Click Choose Files and select multiple files from your computer

Endpoint: POST http://localhost:8000/api/upload-files/
GitHub Repository: https://github.com/itstuffsolutions/how-to-upload-multiple-files-in-laravel-api-using-postman
Conclusion
In this Laravel 12 tutorial, you learned how to build a complete and secure multiple file upload API and test it effectively using Postman. We covered everything from creating the database structure and configuring storage to implementing robust validation rules and handling file uploads inside a controller. By validating both the file array and each individual file, you ensured better security, clearer error handling, and a more reliable API for real-world use cases.
This approach is ideal for applications like galleries, document management systems, and any platform that requires uploading multiple files through an API. You can further enhance this setup by adding authentication, cloud storage (such as AWS S3), file type categorization, or soft deletes. With this foundation, you’re now well-equipped to handle multiple file uploads confidently in your Laravel APIs.

