In this Laravel 12 tutorial titled “Laravel 12: How to Import Large CSV Files 10x Faster”, you will learn how to import large csv files very fast without using any package.
When working with large CSV files (hundreds of thousands or millions of rows), Laravel’s traditional import methods like DB::table()->insert() or Excel packages can become slow and memory-hungry. In such cases, MySQL raw queries provide the fastest possible way to import data in Laravel.
MySQL’s LOAD DATA INFILE or LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE bypasses PHP processing entirely, reading files directly into the database at high speeds—up to 10x faster for millions of rows.
This approach suits Laravel developers handling bulk data from user uploads or exports, avoiding timeouts and high resource use.
Table of Contents
Why Normal CSV Imports Are Slow in Laravel
Common Laravel import approaches:
- DB::table()->insert()
- Eloquent models
- Laravel Excel (Maatwebsite)
These methods:
- Process data row by row or in chunks
- Consume PHP memory
- Add framework overhead
For small to medium files, this is fine.
For large CSV files, performance drops drastically.
What Is LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE?
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE is a native MySQL command that imports CSV data directly into a table, bypassing PHP entirely.
Key benefits:
- Extremely fast (10–50x faster)
- Minimal memory usage
- Ideal for bulk imports
When Should You Use MySQL Raw CSV Import?
Use it when:
- CSV file is very large
- You want maximum performance
- Data structure already matches the database table
- You’re using MySQL or MariaDB
- Import is a one-time or batch operation
Avoid it when:
- You need validation or transformations per row
- You must hash passwords with Hash::make()
- Database is SQLite or PostgreSQL
- File size is small (overkill)
Prerequisites and Configuration
Enable MySQL local_infile
In my.ini or my.cnf:
[mysqld]
local_infile=1
[client]
local_infile=1
Restart MySQL.
Enable PDO Option in Laravel
Enable local_infile in Laravel’s config/database.php:
'mysql' => [
// ...
'options' => [
PDO::MYSQL_ATTR_LOCAL_INFILE => true,
],
],
Restart your server and clear config cache with:
php artisan config:clear
Read Also : How to Import Large Excel and CSV Files in Laravel 12 Complete Guide
Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1: Create a controller
In this step, we will create a controller and define a method to handle the file upload and data import.
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Models\User;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;
class UserController extends Controller
{
public function index(){
$users = User::orderBy("id")->paginate(10);
return view('import',compact('users'));
}
/**
* Import data from Excel/CSV
*/
public function import(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'file' => 'required|mimes:xlsx,xls,csv',
]);
try {
$filePath = addslashes(
str_replace('\\', '/', $request->file('file')->getRealPath())
);
DB::table('users')->truncate();
// Disable checks for speed
DB::statement('SET @@session.unique_checks = 0');
DB::statement('SET @@session.foreign_key_checks = 0');
DB::statement("
LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE '{$filePath}'
IGNORE
INTO TABLE users
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ','
ENCLOSED BY '\"'
LINES TERMINATED BY '\r\n'
IGNORE 1 LINES
(@column1,@column2,@column3)
SET name=@column2,email=@column3,created_at = NOW(), updated_at = NOW()
");
// Re-enable checks
DB::statement('SET @@session.unique_checks = 1');
DB::statement('SET @@session.foreign_key_checks = 1');
unlink($filePath); // Clean up
return back()->with('success', 'Users Imported successfully!');
} catch (\Exception $e) {
return back()->with('error', 'Error importing file: ' . $e->getMessage());
}
}
}
Explanation:
- ->truncate():Deletes all existing users, Resets AUTO_INCREMENT
- Skips uniqueness & foreign key checks temporarily , Makes bulk import much faster,Only safe if your CSV is trusted.
- LOCAL INFILE: read file from client
- IGNORE: skip duplicate rows
- FIELDS TERMINATED BY ‘,’: CSV separator
- LINES TERMINATED BY ‘\r\n’: Windows-style line ending
- ENCLOSED BY ‘”‘: handles quoted CSV values
- IGNORE 1 LINES: skips CSV headers
- @column1:Temporary variable (ignored)
- SET name=@column2:Maps CSV column to DB column
- unlink($filePath);:Removes uploaded file from temp directory,Prevents disk clutter
id is not mentioned, so MySQL auto-increment works correctly.
Step 2: Create Routes
In this step, you will register routes to handle file uploads and render the imported data.
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
use App\Http\Controllers\UserController;
Route::controller(UserController::class)->group(function(){
Route::get('users', 'index')->name('users.index');
Route::post('users/import', 'import')->name('users.import');
});
Read Also: Laravel 12 with Vue.js Complete Setup Guide for Beginners
Step 3: Create View
In this step, we will define routes for uploading the file and viewing the imported data.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>How to Import Large Excel and CSV Files in Laravel 12 Complete Guide</title>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.8/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container mt-5">
<div class="card">
<h5 class="card-header">How to Import Large Excel and CSV Files in Laravel 12 Complete Guide - ItStuffSolutiotions</h5>
<div class="card-body">
<!-- Success/Error Messages -->
@if(session('success'))
<div class="alert alert-success">{{ session('success') }}</div>
@endif
@if(session('error'))
<div class="alert alert-danger">{{ session('error') }}</div>
@endif
@if($errors->any())
<div class="alert alert-danger">
<ul class="mb-0">
@foreach($errors->all() as $error)
<li>{{ $error }}</li>
@endforeach
</ul>
</div>
@endif
<form action="{{ route('users.import') }}" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data" class="mb-4 border p-4 rounded bg-light">
@csrf
<div class="row align-items-end">
<div class="col-md-5">
<label class="form-label fw-bold">Select File (XLSX, CSV)</label>
<input type="file" name="file" class="form-control" required>
</div>
<div class="col-md-3">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary w-100">Import Users</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
<table class="table table-bordered data-table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>Created At</th>
<th>Updated At</th>
</tr>
</thead>
@forelse($users as $user)
<tr>
<td>{{ $user->id }}</td>
<td>{{ $user->name }}</td>
<td>{{ $user->email }}</td>
<td>{{ $user->created_at->format('d M Y') }}</td>
<td>{{ $user->updated_at->format('d M Y') }}</td>
</tr>
@empty
<tr>
<td colspan="5" class="text-center">No Users Found!!</td>
</tr>
@endforelse
</table>
<!-- Pagination -->
<div class="d-flex justify-content-center">
{{ $users->links() }}
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.8/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Step 4: Run The Application To Import CSV Data
Once all the steps are completed successfully, start the Laravel development server.
php artisan serve
Next, open your browser and navigate to http://127.0.0.1:8000/users.
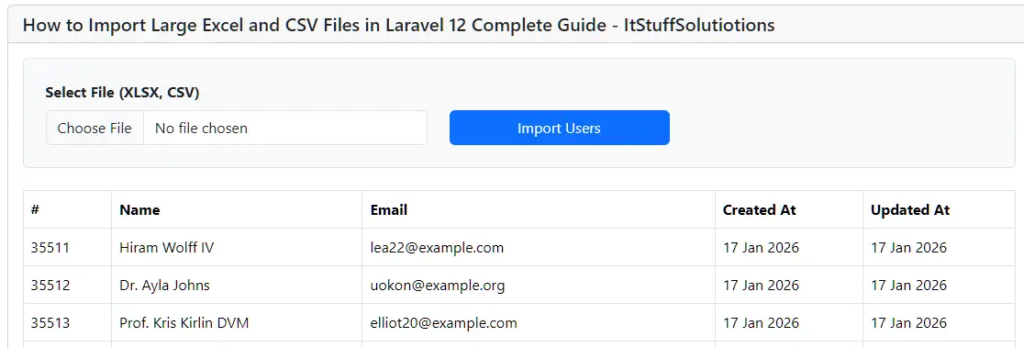
Select the CSV file you want to import, and you will see how quickly the data is imported into your database table.
When NOT to Use MySQL Raw Import
- Small CSV files
- Complex data mapping
- Multiple relations
- Cross-database support needed
- Real-time user uploads
In such cases, use:
- DB::table()->insert()
- Laravel Excel
- LazyCollection
Conclusion
In this Laravel 12 tutorial, you learned how to import large CSV files 10x faster by using MySQL’s native LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE command instead of traditional Laravel import methods or third-party packages. This approach completely bypasses PHP row-by-row processing and allows MySQL to read and insert data directly into the database, making it ideal for handling hundreds of thousands or even millions of records efficiently.
By configuring MySQL and Laravel correctly and executing a raw SQL query with DB::statement(), you can significantly reduce memory usage, avoid timeouts, and achieve maximum import performance. This technique is especially useful for bulk data migrations, admin-only imports, and batch processing tasks where validation and per-row transformations are not required.
However, performance always comes with trade-offs. For small files, complex validations, password hashing, or multi-database support, Laravel’s standard methods like DB::table()->insert(), Eloquent, or Laravel Excel remain the better and safer choice.
In short, when speed and scalability matter most, MySQL raw CSV imports are the best solution in Laravel 12. Use the right tool for the right scenario, and you’ll be able to handle large datasets efficiently without sacrificing application stability.

