In this Laravel 12 tutorial titled “Laravel 12 Create Custom Error Page Example”, you will learn how to create custom error pages step by step with practical examples.
Error pages play an important role in improving user experience and giving meaningful feedback when something goes wrong in your application. Laravel provides a simple and powerful way to customize error pages. In this tutorial, we will learn how to create custom error pages in Laravel 12 for HTTP status codes like 404, 500, 403, and more.
By the end of this guide, you will be able to fully customize error pages to match your application design or branding.
Table of Contents
What Are Custom Error Pages?
Custom error pages replace Laravel’s default error responses with branded, user-friendly pages that maintain consistency with your application’s design. They help users understand what went wrong and guide them back to useful parts of your application.
Why Custom Error Pages Are Important?
Default error pages are simple and not user-friendly. Customizing them helps you:
- Show professional-looking error pages
- Improve user experience
- Provide helpful links to users
- Maintain consistent branding
- Explain what went wrong clearly
Step-by-Step Guide to Laravel 12 Create Custom Error Page Example
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have:
- PHP 8.3 or higher
- Laravel 12 installed
Laravel loads error views automatically from the folder: resources/views/errors/ If the view matching the error code exists, Laravel displays it instantly.
Read Also : Laravel 12 RouteServiceProvider Configuration Tutorial
Step 1: Create the Errors Page
In this step, you will learn two different approaches to creating custom error pages in Laravel 12. You can either create the error page files manually or publish Laravel’s default error templates and customize them according to your needs.
Option 1: Manually Create the Error Pages Directory
Ensure that the following directory exists in your project:
resources/views/errors/
If it does not exist, create it manually.
Once the folder is ready, create the specific error page file you want to customize. For example:
Create a Custom 404 Error Page
Create the file: resources/views/errors/404.blade.php
Create a Custom 500 Error Page
File path: resources/views/errors/500.blade.php
You can similarly create files for other error codes such as 403, 419, or 503, depending on your requirements.
Option 2: Publish Laravel’s Default Error Page Templates
Laravel comes with built-in default error page templates. To customize them, publish them to your project first:
php artisan vendor:publish --tag=laravel-errors
This command copies all default error page templates to resources/views/errors/ directory. After running this, you’ll have access to error views including:
- 401.blade.php – Unauthorized
- 403.blade.php – Forbidden
- 404.blade.php – Not Found
- 419.blade.php – Page Expired
- 429.blade.php – Too Many Requests
- 500.blade.php – Server Error
- 503.blade.php – Service Unavailable
You can now edit any of these files to match your application’s design.
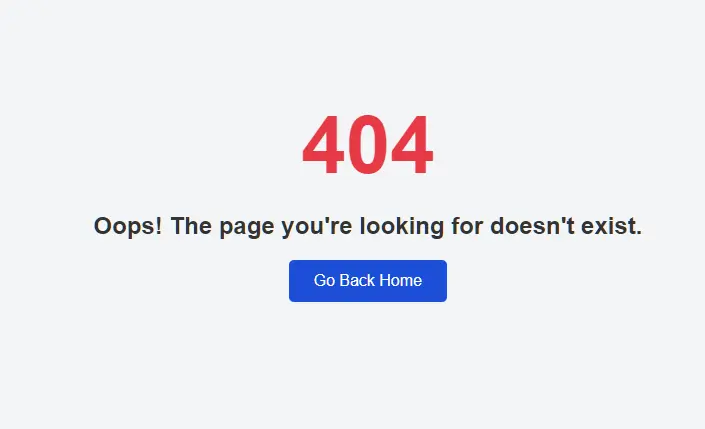
Step 2: Update 404 Error Page Design
Navigate to resources/views/errors/ and edit 404.blade.php:
Update the file with a custom design. For example, you can use the following template:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>404 - Page Not Found</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
background: #f3f4f6;
color: #333;
text-align: center;
}
.container {
margin-top: 10%;
}
h1 {
font-size: 80px;
font-weight: 700;
margin-bottom: 10px;
color: #e63946;
}
h2 {
font-size: 24px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
a {
display: inline-block;
padding: 12px 25px;
background: #1d4ed8;
color: #fff;
border-radius: 5px;
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 16px;
}
a:hover {
background: #2563eb;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>404</h1>
<h2>Oops! The page you're looking for doesn't exist.</h2>
<a href="{{ url('/') }}">Go Back Home</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Step 3: Update a Custom 500 Error Page
Navigate to resources/views/errors/ and edit 500.blade.php:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>500 - Server Error</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
background: #f3f4f6;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
text-align: center;
color: #333;
}
.container {
margin-top: 10%;
}
h1 {
font-size: 80px;
font-weight: bold;
color: #d90429;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
h2 {
font-size: 24px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
p {
font-size: 16px;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
a {
padding: 12px 25px;
background: #1d4ed8;
color: #fff;
text-decoration: none;
border-radius: 5px;
font-size: 16px;
}
a:hover {
background: #2563eb;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<h1>500</h1>
<h2>Internal Server Error</h2>
<p>Something went wrong on our end. Please try again later.</p>
<a href="{{ url('/') }}">Go Back Home</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>

Read Also : Laravel 12 Restrict/Block User Access from IP Address
Tip: Use Blade Layouts for Better Design
If your app uses a layout like layouts.app, you can include it:
@extends('layouts.app')
@section('content')
<div class="text-center py-5">
<h1>404</h1>
<p>Page Not Found</p>
</div>
@endsection
This keeps your error pages consistent with your website theme.
Conclusion
Custom error pages are an essential part of building polished and user-friendly Laravel applications. With Laravel 12, creating and customizing these views is incredibly simple—whether you build them manually or publish Laravel’s default templates.
By customizing pages like 404, 500, 403, and more, you can improve navigation, guide users effectively, and keep your brand identity consistent even when errors occur.
With just a few steps, you can turn technical error screens into helpful, visually appealing pages that enhance the overall experience of your web application.

