When working with large datasets in Laravel applications, pagination is essential for performance and usability. Laravel ships with a powerful paginator that works seamlessly with Eloquent and the query builder, making it extremely easy to break records into manageable chunks.
But traditional pagination reloads the entire page with each click. In modern applications, that full page reload can feel slow and clunky.
Pagination is a must-have feature in modern web applications. In this Laravel tutorial, you’ll learn Laravel 12 pagination using jQuery AJAX Step-by-Step Guide in a simple, practical, and beginner-friendly way. By the end, you’ll be able to load paginated data dynamically without refreshing the page—clean, fast, and professional.
Table of Contents
What Is AJAX Pagination and Why Use It?
AJAX pagination allows users to load new records without refreshing the entire page. In Laravel 12 pagination using jQuery AJAX, this means:
- Faster page loads
- Better user experience
- Cleaner navigation
- Reduced server load
Instead of reloading a full page, only the data section updates dynamically.
Prerequisites for Laravel 12 Pagination
Before starting, make sure you have:
- PHP 8.2+
- Composer installed
- Laravel 12
- Basic knowledge of Blade, jQuery, and MVC
- MySQL or any supported database
Step 1: Create a New Laravel 12 Project
If you already have a Laravel 12 project, you can skip this step.
composer create-project laravel/laravel laravel12-ajax-pagination
cd laravel12-ajax-pagination
Step 2: Configure Database and Migration
Configure your .env with your database settings:
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=laravel12_ajax_pagination
DB_USERNAME=root
DB_PASSWORD=
Run migrations just to ensure everything is wired correctly:
php artisan migrate
Step 3: Seed Dummy Data (Recommended)
In this step, we are directly inserting data into the users table because Laravel provides a UserFactory by default. This means we only need to run the seeder without creating a custom factory.
If you are using a model other than User, you will need to create a factory for that model. You can follow my detailed tutorial here:
Read Also : Laravel 12 Database Seeder Example
To see pagination working properly, you’ll need a sufficient amount of data in the database. For this purpose, we’ll use Laravel Tinker:
php artisan tinker
User::factory()->count(100)->create();
Now you have 100 users to paginate.
Step 4: Define Routes
Open routes/web.php:
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
use App\Http\Controllers\UserController;
Route::get('users/list', [UserController::class,'index'])->name('ajax.pagination');
Read Also : Laravel 12 Import Very Large CSV into Database With Seeder
Step 4: Create Controller
Generate a controller:
php artisan make:controller UserController
Open app/Http/Controllers/UserController.php:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Models\User;
class UserController extends Controller
{
public function index(Request $request){
$users = User::orderBy("id")->paginate(5);
if($request->ajax())
{
return view('pagination', compact('users'))->render();
}
return view('list',compact('users'));
}
}
Explanation
- Uses $users = User::orderBy(“id”)->paginate(5); ensures the records are fetched in a consistent ascending order based on the primary key and limits the result set to 5 users per page and automatically handles page offsets using the request’s page query parameter.
- Detects AJAX via $request->ajax()
- For AJAX, returns only the rendered partial so jQuery can inject it into the page
- ->render() converts a Blade view into a pure HTML string so your AJAX call receives exactly the markup your JavaScript expects — no more, no less.
- For normal requests, returns the full page view
Step 5: Create Blade Views for AJAX Pagination
You’ll use:
- A main (parent) view (list.blade.php) that contains the page layout and a container where data will be loaded.
- A small partial view (pagination.blade.php) that displays the users list/table along with pagination links.
Create the Main View
Create resources/views/list.blade.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Laravel 12 Simple Pagination Step-by-Step Tutorial</title>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.8/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container mt-5">
<div class="card">
<h5 class="card-header bg-primary text-white">Laravel 12 Simple Pagination Step-by-Step Tutorial - ItStuffSolutiotions</h5>
<div class="card-body ">
<div class="table_data">
@include('pagination')
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.8/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/jquery/2.1.4/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$(document).on('click', '.pagination a', function(event){
event.preventDefault();
var page = $(this).attr('href').split('page=')[1];
get_data(page);
});
function get_data(page)
{
$.ajax({
url:"{{route('ajax.pagination')}}?page="+page,
success:function(data)
{
$('.table_data').html(data);
}
});
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Create the Partial View
Create resources/views/pagination.blade.php
<table class="table table-bordered ">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>#</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>Created At</th>
<th>Updated At</th>
</tr>
</thead>
@forelse($users as $user)
<tr>
<td>{{ $user->id }}</td>
<td>{{ $user->name }}</td>
<td>{{ $user->email }}</td>
<td>{{ $user->created_at->format('d M Y') }}</td>
<td>{{ $user->updated_at->format('d M Y') }}</td>
</tr>
@empty
<tr>
<td colspan="5" class="text-center">No Users Found!!</td>
</tr>
@endforelse
</table>
<!-- Pagination -->
{!! $users->withQueryString()->links('pagination::bootstrap-5') !!}
Explanation
- When the page loads for the first time, Laravel uses @include(‘pagination’) to show the data normally from the server.
- Pagination links are generated by {!! $users->withQueryString()->links(‘pagination::bootstrap-5’) !!} in the pagination view.
- When a user clicks .pagination a, jQuery catches the click before the page reloads and sends an AJAX GET to load the new page data.
- The AJAX success callback replaces only .table_data content, not the whole page, so everything feels fast and smooth.
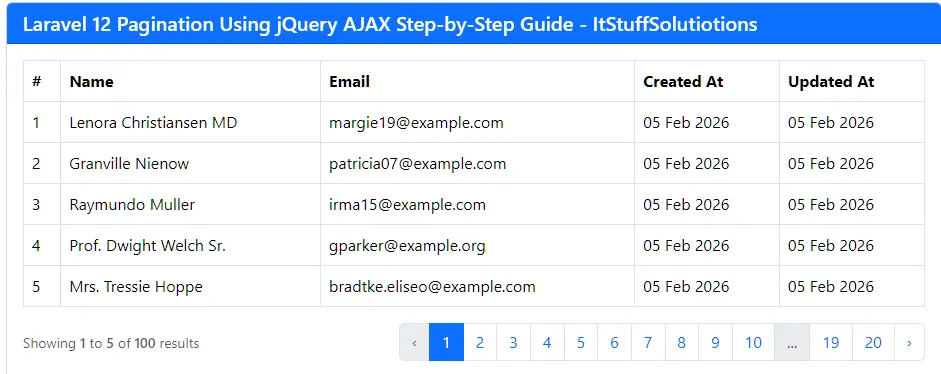
Step 6: Test AJAX Pagination
All the steps have been completed successfully. Now, run your Laravel application:
php artisan serve
Open in browser:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/list
Click on pagination links, no page reload, just smooth data loading.
Step 7: Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Entire Page Renders Inside Container
If you see the whole HTML page being injected into .table_data, it usually means:
- Your controller returned the full view, not just the partial, even for AJAX requests.
- Fix: Ensure you have the if ($request->ajax()) condition returning the partial only.
Pagination links reload the whole page
Use e.preventDefault() in jQuery to stop the default link behavior.
$(document).on('click', '.pagination a', function (e) {
e.preventDefault();
});
404 error when clicking pagination links
Make sure the route URL in AJAX matches the route defined in web.php.
CSRF Errors (Mostly with POST/PUT/DELETE)
GET requests usually don’t require CSRF tokens. If you switch pagination to POST or use filter forms that submit via AJAX, ensure the CSRF token is added to headers:
$.ajaxSetup({
headers: {
'X-CSRF-TOKEN': $('meta[name="csrf-token"]').attr('content')
}
});
And keep the <meta name=”csrf-token”> tag in your <head>.
Conclusion
Implementing Laravel 12 pagination using jQuery AJAX is one of the best ways to enhance user experience without adding complexity. With minimal code and maximum performance, AJAX pagination keeps your app modern, responsive, and professional.
Start using this approach today and take your Laravel 12 applications to the next level.
FAQs
Q1: Is jQuery required for Laravel 12 pagination using jQuery AJAX?
Yes, in this guide jQuery is used, but you can also use Fetch API or Axios.
Q2: Can I use this with Livewire or Vue?
Yes, but this tutorial focuses on jQuery AJAX for simplicity.
Q3: Is Laravel 12 pagination secure?
Yes, Laravel handles pagination securely by default.
Q4: Can I reuse this logic in other projects?
Absolutely. This pattern works across all Laravel versions with minor changes.

