In this laravel tutorial titled “laravel 12 clear cache, route, config, event command” we will see how to clear cache, route, config, view, and event cache in Laravel 12—step-by-step.
Laravel’s caching system is designed to improve application performance by temporarily storing frequently accessed data. This reduces the need to repeatedly process the same information or run costly database queries. Laravel makes caching simple and flexible, with support for popular backends such as Redis, Memcached, and even database-driven storage.
During development or after deployment, cached data—such as routes, configuration files, or views—can sometimes cause unexpected behavior. For example, I once tried accessing a value from a config variable, but it kept returning null, even though the value was correctly set. After some debugging, I realized the issue was due to Laravel using cached config data. Once I cleared the config cache, the correct value started showing up. Fortunately, Laravel provides built-in Artisan commands to easily clear different types of cache and resolve such issues quickly.
When you’re working on a Laravel project, you might encounter situations like:
- Modify .env or config files and nothing happens
- Alter Blade views and still see the old version
In such cases, Laravel’s cached files are likely the reason. Removing the relevant cache files usually fixes these problems right away.
Laravel 12 Clear Cache, Route, Config, Event Command
1. Clear Application Cache
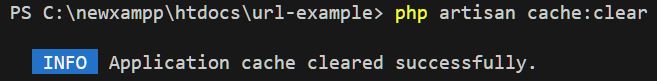
This command clears all of the application cache. It’s used to remove the entire cache stored by the application.
php artisan cache:clear
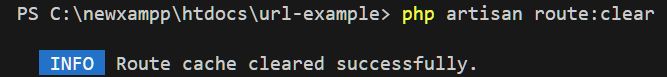
2. Clear Route Cache
This command clears the cached routes file. Use it after editing your web.php or api.php routes, especially when changes are not reflecting in your application.
php artisan route:clear
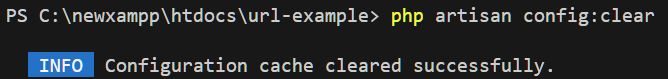
3. Clear Config Cache
This command clears the cached configuration values. Useful after editing .env or any config files inside config/.
php artisan config:clear
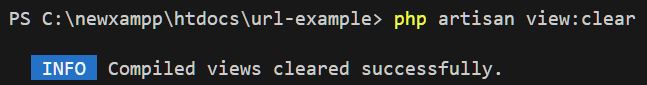
4. Clear View Cache
This command removes all compiled Blade templates inside storage/framework/views. This ensures that any changes in views are freshly compiled.
php artisan view:clear
5. Clear Event Cache
This command clears cached events and listeners. This is especially helpful when you’ve modified or added new event listeners and Laravel isn’t detecting them.
php artisan event:clear
6. Clear All Caches
The optimize:clear command can be used to remove all cache files—including configuration, events, routes, and views—as well as clear all keys stored in the default cache driver.
php artisan optimize:clear
7. Clear Cache Using Route
This route allows you to clear the cache through a browser without command. It’s useful when you don’t have access to the command line. However, avoid using this in a production environment without proper authentication and security, as it can create a serious vulnerability.
<?php
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Artisan;
Route::get('/cache-clear', function () {
Artisan::call('cache:clear');
return 'Application cache cleared!';
});
Read Also : Laravel 12 Rollback a Specific Migration
Rebuild Cache Files
After clearing caches, you can optionally rebuild them:
1. Rebuild Config Cache
Generates a cache file for your configuration settings.
php artisan config:cache
2. Rebuild Route Cache
Creates a cached version of your application routes.
php artisan route:cache
3. Rebuild Event Cache
Caches your event and listener mappings.
php artisan event:cache
4. Rebuild View Cache
Compiles and caches all Blade templates.
php artisan view:cache
5. Cache All at Once Using Optimize
Caches the framework bootstrap files, configuration, and other metadata to optimize performance.
php artisan optimize
Conclusion:
Keeping caches under control is essential for a stable and fast Laravel 12 application. With a clear understanding of what each command does, it’s straightforward to flush only what’s needed during development and to rebuild optimized caches for production. Use cache:clear for the application cache store, and remember that config:clear, route:clear, view:clear, and event:clear target Laravel’s compiled files separately. For quick maintenance, optimize:clear safely wipes all caches at once, while optimize or the individual cache commands rebuild performance-ready artifacts for live environments.
In practice: clear selectively while iterating locally; after deployments, rebuild caches intentionally (config:cache, route:cache, view:cache, event:cache or simply optimize). If changes don’t reflect, it’s almost always a cached config or routes file—clear and re-cache. Following these habits ensures predictable behavior, fewer “why isn’t this updating?” moments, and consistently snappy performance in production.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1: What’s the fastest way to clear all caches at once?
Run php artisan optimize:clear to clear all cached files, routes, config, views, events, and application cache in one command.
Q2: What’s the difference between cache:clear and optimize:clear?
cache:clearonly flushes application cache stored in your cache driver (Redis, file, etc.),optimize:clearremoves compiled files AND clears the application cache.
Q3: Which caches does optimize:clear actually clear?
Configuration cache, route cache, view cache, event cache, application cache, and compiled class files.
Q4: How do I clear the application cache?
Use php artisan cache:clear to flush all cached data from your default cache store.
Q5: Can I clear cache from a specific store?
Yes, use php artisan cache:clear –store=redis to target a specific cache driver.
Q6: Where is the application cache stored?
File-based cache is stored in storage/framework/cache/data/.
Q7: When should I clear config cache?
After updating .env files, config/*.php files, or environment variables.
Q8: What’s the difference between config:clear and config:cache?
config:clear removes cached config files.
config:cache rebuilds the config cache for production performance.
Q9: Why don’t my .env changes reflect?
Configuration is cached; run php artisan config:clear then php artisan config:cache to apply changes.
Q10: When should I rebuild route cache?
After adding/modifying routes in production, run php artisan route:cache for performance.
Q11: Can I clear route cache on shared hosting?
Yes, use SSH/terminal or create a temporary route that calls Artisan::call(‘route:clear’) then remove it.
Q12: How do I clear compiled Blade views?
Run php artisan view:clear to delete cached templates from storage/framework/views.
Q13: Do I need to rebuild view cache manually?
No, Laravel automatically recompiles views when needed, but you can precompile with php artisan view:cache.
Q14: When do I need to clear event cache?
After modifying event listeners or when using php artisan event:cache in production.
Q15: Why does cache:clear work sometimes but not others?
Permission conflicts between CLI user and web server user; run commands as the same user: sudo -u www-data php artisan cache:clear.
Q16: I get “Failed to clear cache. Make sure you have appropriate permissions”—how to fix?
Check if storage/framework/cache/data folder exists, create it if missing, or run sudo chown -R www-data:www-data storage and sudo chmod -R 775 storage.
Q17: Can I clear cache via routes/controllers?
Yes, but secure the route: Artisan::call(‘cache:clear’) in a protected controller method.
Q18: Is it safe to add public cache-clearing routes?
Only if properly protected/authenticated; avoid public access to prevent abuse.
Q19: My changes still don’t show after clearing cache—what else?
Also run composer dump-autoload for autoloader issues, check file permissions, or try php artisan optimize:clear followed by php artisan optimize.
Q20: Should I use different cache drivers for different purposes?
Yes, Redis for sessions/queues, file cache for config, database cache for application data based on your needs.
Q21: What’s the recommended deployment workflow?
Production: php artisan config:cache, route:cache, view:cache, event:cache or simply php artisan optimize.
Q22: Should I use cache:clear in production?
Use carefully; rebuild only the caches you need (like config or route) instead of clearing everything for no reason.
Q23: How often should I clear cache during development?
For production, run: php artisan config:cache, route:cache, view:cache, event:cache or or simply php artisan optimize

